Introduction
Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly changing various aspects of human life, presenting both challenges and opportunities for jobs and education. As AI evolves, it is crucial to understand its effects on employment sectors and the educational landscape. AI’s impact necessitates adapting education systems to align with the digital age, ensuring individuals can navigate the evolving job market.
Understanding Artificial Intelligence and its Impact
Artificial intelligence is rooted in enabling machines to solve complex problems in ways that mimic human cognition, drawing heavily on mathematical principles and algorithms. Recent advancements, particularly in large language models (LLMs), have highlighted the power of neural networks. These networks, modeled after the human brain, use interconnected nodes in layered structures. Machine learning is an essential component, identifying patterns in data to allow algorithms to discern valuable insights. As AI’s influence expands, decision-making within organizations and overall efficiency are significantly enhanced. Here are types of AI applications in day-to-day life as exemplified by highly developed climes:
- Image Recognition: Identifying objects or people in digital images. Examples include labeling X-rays, tagging faces on social media, facial recognition for security, and detecting genetic diseases.
- Generative AI for Education: Distilling complex technological and scientific concepts by adopting chatbots or LLMs is becoming the norm.
- Speech Recognition: Translating spoken language into text. Used in voice search, voice dialing, and virtual assistants like Google Home and Amazon Alexa.
- Medical Diagnosis: Assisting in diagnosing diseases by discerning patterns in symptoms. This can involve analyzing bodily fluids, oncology, pathology, and identifying phenotypes correlated with rare genetic diseases.
- Predictive Analytics: Classifying data and defining it with rules set by data analysts to calculate the probability of an action13.
- Virtual Personal Assistants: Combining speech recognition and machine learning to respond to voice commands, provide information, and control devices. Examples include Siri, Google Assistant, and Alexa.
- Social Media Features: Personalizing news feeds, suggesting connections, and improving ad targeting based on user activity, likes, and comments.
- Product Recommendations: Tracking user behavior (previous purchases, searches, cart history) to suggest products on e-commerce websites.
- Transportation: Optimizing routes, predicting arrival times, and matching riders with drivers in ride-sharing apps like Uber and Lyft. Computer vision in self-driving cars enables real-time decision-making.
- Smartphone Applications: Powering facial recognition, voice assistants, and camera features like image enhancement and object detection.
- Customer Service: Understanding customer tone and directing them to appropriate customer service agents.
- Lead Generation and SEO: Identifying potential customers and optimizing online searches.
- Helping the homeless: Matching homeless citizens with available resources with complex AI algorithms
- Video Surveillance: Detecting unusual behavior to detect crime.
- Customized Healthcare: Analyzing patient records and genetic make-up to recommend treatment plans or medicine.
- Target Recognition: Identifying potential targets from aerial or satellite imagery.
- Threat Assessment: Analyzing sensor data to detect and classify potential threats (e.g., missile launches, incoming projectiles).
- Autonomous Vehicles: Controlling unmanned aerial vehicles (drones), ground vehicles, and naval vessels.
- Cybersecurity: Detecting and responding to cyberattacks with AI alogorithms.
- Predictive Maintenance: Predicting equipment failures to optimize maintenance schedules and reduce downtime.
- Logistics Optimization: Optimizing supply chains and resource allocation.
- Training Simulations: Creating realistic training environments for trainees in mission critical fields.
- Intelligence Analysis: Analyzing vast amounts of data to identify patterns and insights relevant to national growth and security.
The Impact of AI on Jobs and the Economy
AI is expected to create new job opportunities while automating routine tasks. McKinsey & Company projects that AI could generate 20 to 50 million new jobs globally by 2030, particularly in healthcare, manufacturing, and finance, requiring skills such as critical thinking, creativity, and problem-solving. While AI will certainly displace jobs, particularly those involving repetitive tasks, the World Economic Forum predicts a net gain of 58 million jobs globally by 2025, with 133 million new jobs created against 75 million jobs displaced. This shift highlights the importance of adapting to technological changes and seizing new employment opportunities in the digitized economy.
AI in Education
The integration of AI tools in education is becoming increasingly essential, enhancing students’ abilities to analyze data, automate tasks, and innovate. For instance, AI can personalize learning by tailoring educational content to individual student needs, thereby improving the overall learning experience. AI systems can also automate repetitive administrative tasks in schools, colleges, and universities, such as scheduling, attendance, and record keeping, freeing up educators’ time. Furthermore, AI can offer valuable insights into student performance through data analysis, helping teachers provide early intervention and support.
Historical Context
Understanding the historical context of technological and societal shifts provides valuable perspective on the challenges and opportunities presented by the AI era. Taking a look through the sands of time, the following are significant shifts in the knowledge economy that have shaped the destinies of very wealthy and poor counties:
- Scholastic Era (1100–1700 AD): This era emphasized critical thinking and problem-solving. While these skills remain relevant, Nigeria’s education system often focuses on qualifications rather than practical application.
- Industrial Era (1760 AD — Present): The shift to new manufacturing processes transformed economies and societies. Nigeria continues to grapple with industrialization, highlighting the need to embrace new technologies and production methods.
- Information Age (1945 AD — Present): The rise of the knowledge industry emphasized entrepreneurship, digital literacy, and awareness. While Nigeria has made progress in these areas, more effort is needed to leverage these opportunities effectively.
- Communication Age (2002 AD — Present): The proliferation of mobile internet and social media has created unprecedented access to information. However, many Nigerians misuse these tools for entertainment rather than productive purposes.
- The AI Era (2020 AD — Present): The increasing capabilities of AI are redefining industries and jobs. Higher education must adapt to focus on discipline, exposure, mentorship, and networking to prepare individuals for this new era.
Africa’s Most Tech-Advanced Countries
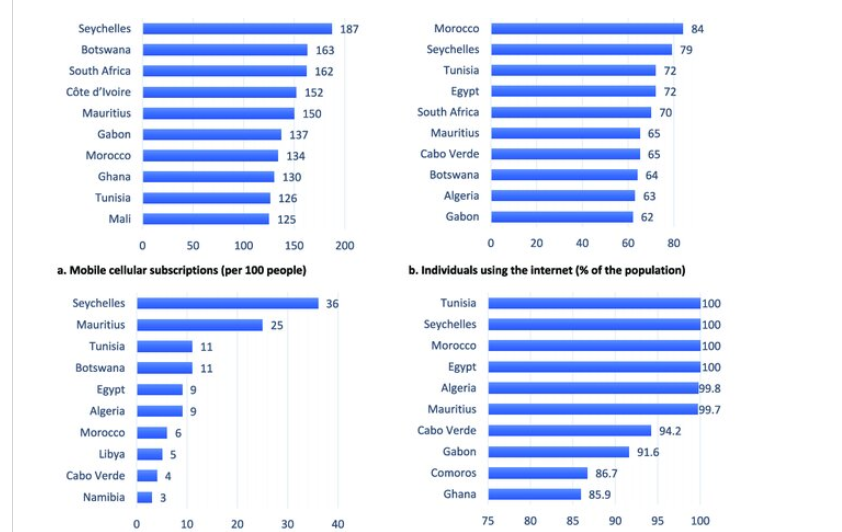
While the continent has faced challenges, many due to ignoring these shifts in knowledge paradigms, several African nations have emerged as leaders in technology adoption. While different reports may vary in their exact rankings, countries like Rwanda, Mauritius, South Africa, and Libya consistently appear near the top in terms of ICT development and AI readiness. Mauritius, for instance, has the highest ranking in Africa for ICT adoption and AI readiness, with a score that places it ahead of countries like Indonesia and Italy. Libya also shows a high internet penetration rate. These nations often have stronger digital infrastructure, more developed regulatory frameworks, and greater investment in digital skills. However, it’s crucial to note that even within these leading countries, disparities in digital access and skills remain a challenge.
Nigeria, despite having the largest population in Africa, lags behind other countries in digital development. According to a report, Nigeria ranks 24th in Africa in terms of digital development, with an ICT index score of 46.91. In contrast, a different report gave Nigeria a score of 71 percent in readiness for digital transformation, highlighting the country’s strong regulatory framework and collaborative governance as positives. Being ot all bad news, to improve her standing, Nigeria must focus on expanding its broadband internet penetration efforts and promoting digital skills.
Deception as a Strategy in the Age of AI
In view of on-going debates while at the same time drawing a parallel to a well known military strategy, it is important to recognize that narratives surrounding AI’s impact can be strategically manipulated in favour or against a nation, and indeed, Nigeria. Downplaying the potential disruption of AI in the job market can be a form of “deception,” that may lull individuals and the nation at large into complacency and hindering necessary preparations. In the “war” for attention and control in the information age, it’s crucial to critically evaluate different perspectives and proactively shape the narrative to ensure informed decision-making and preparedness for the forceful changes AI will bring.
Challenges Facing Nigerian Tech Experts
In a bid to manage the inevitable change, Nigerian tech experts face a complex set of challenges some which have traditionally hindered the country’s overall digital transformation efforts. These challenges include:
- Educational gaps: The educational system often emphasizes theoretical knowledge over practical skills, leaving university graduates ill-prepared for the demands of the tech industry.
- Infrastructure: Inadequate infrastructure, including limited access to reliable electricity and internet connectivity, impedes technological progress.
- Funding: Insufficient government funding for research and development, startups, and technology initiatives limits innovation and growth.
- Culture: Societal attitudes that do not fully embrace innovation and entrepreneurship tend to striffle creativity and risk-taking.
- Policy: Inconsistent government policy directions, corruption and political instability are major deterrents for investors in the technology sector.
To overcome these challenges, Nigeria needs a paradigm shift that prioritizes practical skills, fosters a culture of innovation, and creates a stable and supportive environment for tech businesses to thrive. Under the present administration, the country is seen to be focusing on expanding its fiber optic network and promoting digital skills which are necessary strides towards an AI dominated future.
Strategies for Navigating the AI Revolution while remaining relevant
The AI revolution is poised to transform the tech industry and potentially render some traditional roles obsolete. In this dynamic environment, individuals and organizations must embrace these proactive strategies to thrive:
- Becoming Solution Providers: Focusing on addressing real-world challenges, target the indigenous landscape.
- Embracing Continuous Learning: Committing to staying informed and skilled amidst rapid technological advancements.
- Prioritizing Focus and Imagination: Avoiding distractions and leveraging imagination in problem-solving.
- Strategic Use of AI Tools: Utilizing AI to augment innate capabilities without becoming overly reliant on imported or third party solutions.
Essential Skills for the AI Age
Adapting education to changing occupations is crucial to prepare the future workforce for the demands and challenges presented by AI. A relevant and up-to-date curriculum that fosters skills like engineering, programming, data analysis, critical and creative thinking, problem-solving, and collaboration must be prioritized. Education must encourage critical and innovative thinking to enable individuals to adapt to change and generate innovative solutions in new occupations. Incorporating AI tools into the curriculum can equip graduates with the skills to navigate the complexities of modern careers and thrive in a dynamic professional landscape.
To thrive in Nigeria’s AI-influenced job market, developing a combination of technical and soft skills is essential. The following skills are particularly paramount:
Creativity: AI and automation can handle routine tasks, but creativity remains a uniquely human skill. Nigerians need to foster their creative abilities to develop innovative solutions and strategies that can’t be replicated by AI. This includes thinking outside the box, generating new ideas, and approaching problems from unconventional angles. Every institution should adopt a “Creative Shop” where great ideas are routinely experimented.
Emotional Intelligence (EI): As workplaces become more technologically driven, EI is increasingly important. EI involves understanding and managing one’s own emotions and those of others. In the Nigerian context, where collaboration and communication are vital, EI can foster positive relationships, enhance teamwork, and create a more harmonious work environment. Being a soft skill, all institutions must inculcate EI in their ethos.
Adaptability: The AI landscape is constantly evolving. Nigerians must be adaptable and willing to learn new technologies, tools, and methodologies. This includes staying updated with the latest AI trends, being open to change, and embracing lifelong learning. Adaptability attitude tests should be programmed into the general curriculum.
Critical Thinking: While AI can process vast amounts of data, human judgment and critical thinking are necessary to interpret AI-generated insights and make strategic decisions. Generally, Nigerian youths need to develop their critical-thinking abilities to analyze complex information, identify biases, and draw well-reasoned conclusions.
Problem-Solving: AI can assist with problem-solving, but humans are still needed to define problems, develop solutions, and implement them effectively. Young Nigerians must be trained to enhance their problem-solving skills to tackle complex challenges, especially in collaboration with AI systems.
Leadership: As AI transforms the workplace, strong leadership skills are essential to guide teams, manage change, and foster a culture of innovation. Nigeria future leaders need to be able to inspire, motivate, and empower their teams to embrace AI and leverage its potential. Leadership thus becomes a top priority for any knowledge transfer scheme.
Communication: Effective communication is crucial for conveying complex ideas, collaborating with diverse teams, and building consensus. Nigerian youths need to hone their communication skills to articulate their thoughts clearly, actively listen to others, and foster open dialogue, either virtually or physically.
Collaboration: Adopting AI systems for building large scale solutions usually demand different perspectives from various professionals, including software engineers, data scientists, and business analysts. Nigerian youths need have their collaboration skills enhanced to work effectively in teams, share knowledge, and co-create innovative solutions.
Prompt Engineering: The ability to effectively communicate with AI systems through well-crafted prompts will become increasingly valuable as LLM models are further developed. Nigerian youths should be trained to distill difficult or laborious concepts with AI with prompts.
First Principle Concepts: It’s also crucial to emphasize foundational learning, including basic literacy and numeracy. These skills provide a base for acquiring more advanced, automation-resistant competencies. And even the platforms or forums for these basic education can be enhanced with AI.
Financial Literacy and Prudent Decision-Making: Understanding financial principles, managing resources effectively, and making informed decisions about investments and expenditures are essential skills in an AI age for building financial stability and navigating economic uncertainties.
Survival Skills: Our youth must acquire ability to organize resources efficiently and thrive despite scarcity or hardship, whether due to circumstance or strategic choice.
Emerging Tech Opportunities in the AI Landscape
The AI era offers Africa immense opportunities to pioneer new frontiers, particularly by strengthening its foundation in core technological infrastructures and dependencies.
- Semiconductor Engineering: Developing home gown capacity for building computer chipsets
- Custom Operating Systems: Developing customized OS solutions based on our indigenous languages, culture and special requirement.
- Original Programming Languages: Creating innovative programming languages to re-imagine software that suites our peculiar requirement.
- Cloud Systems: Establishing tailored cloud solutions to gain complete ownership of our technology assets.
- Embedded Systems: Venturing beyond traditional coding, encouraging massive training and research into hardware-software integration, real-time processing, IoT applications, and AI-driven automation.
- Emerging Technologies: Advancing innovations in electric vehicles (EVs), brain-computer interfaces (BCIs), agrifood technology (AgriTech), digital health solutions (HealthTech), aerospace engineering, industrial automation, mechatronic systems, space exploration technologies, and precision navigation with custom GPS solutions.
Conclusion
Navigating and thriving in the AI era necessitates a strategic blend of discipline, continuous learning, mentorship, and networking. By actively addressing real-world problems, staying well-informed, and responsibly harnessing the power of AI, Nigerian youths can unlock the potential of this technology. Embracing challenges, competing with tenacity, and striving for global excellence are vital. And as Albert Einstein aptly stated, “Imagination is more important than knowledge.” Nigerian youths must divest some of their fervent energies from “Nollywood” to seize moment for technological emancipation with AI.

AI is not just a tool — it’s a force, a companion, a limitless frontier waiting to be conquered. Like Tony Stark and his legendary Jarvis in the Iron Man movie franchise, we have the power to shape the future, to push boundaries, and to redefine what’s possible.
Nigerian youth must embrace AI with courage and purpose. You must innovate with audacity. Let your vision soar beyond limits. Become the architect of tomorrow’s Africa. Be fearless. Be unstoppable. Survive AI.
References
Akinpelu, A. (2023, December 7). Nigeria ranks 24th in digital development in Africa. Punch. https://punchng.com/nigeria-ranks-24th-in-digital-development-in-africa/
After School Africa. (n.d.). Top 10 African countries adopting ICT development. https://afterschoolafrica.com/45110/top-10-african-countries-adopting-ict-development/Claude, J. (2023). Positive outlook for tech adoption by African governments in 2023.
CIO Africa. https://cioafrica.co/positive-outlook-for-tech-adoption-by-african-governments-in-2023/Markoff, J., & Ray, P. (2019). How artificial intelligence is transforming the world.
Brookings. https://www.brookings.edu/articles/how-artificial-intelligence-is-transforming-the-world/
McKinsey & Company. (2023, July 27). AI could upend job market by 2033 according to a McKinsey report. https://www.mckinsey.com/featured-insights/future-of-work/ai-could-upend-job-market-by-2033-according-to-a-mckinsey-report
McKinsey Global Institute. (2023, July 20). The race to deploy generative AI and raise skills. https://www.mckinsey.com/featured-insights/future-of-work/the-race-to-deploy-generative-ai-and-raise-skills
McKinsey Global Institute. (2024, February 15). Generative AI and the future of work in America. https://www.mckinsey.com/featured-insights/future-of-work/generative-ai-and-the-future-of-work-in-america

